-
Services
Health
Beauty
The fractional laser with the Gynolaser applicator is used for treatment of functional disorders in gynecology
and urogynecology such as vaginal dryness, painful intercourse, reduced elasticity of the vaginal walls and initial leakage of urine. Vaginal rejuvenation is a laser surgical procedure that “rejuvenates” the vagina by 10 to 12 years. The applicator is inserted directly into the vagina. The result of the procedure is the narrowing and strengthening of the walls of the vagina and mucous tissue.
Gynolaser also solves stress urinary incontinence and uterine prolapse after childbirth. The advantage of Gynolaser is its speed, simplicity and painlessness.
The operation does not require anesthesia.
If a gynecological examination is impossible, excessively painful or complicated, it is possible to undergo treatment under anesthesia. After putting the patient under anesthesia, gynecological treatment is performed, including the possibility of collecting material for cultivation or cytological examination.

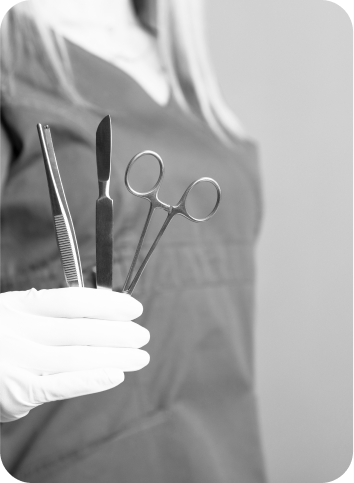
It is an optical examination of the cervical canal and the uterine cavity with option of damaged or suspicious structures removal from the cervical canal or the uterine cavity. Cervix is accessed vaginally. Hysteroscopy is also a medical procedure, during which any unwanted part is removed.
Cervical conization is a surgical procedure that
is performed to remove a cone-shaped piece of tissue
from the cervix. This procedure is often used for diagnostic purposes or to remove unwanted changes
in the tissue of the cervix.

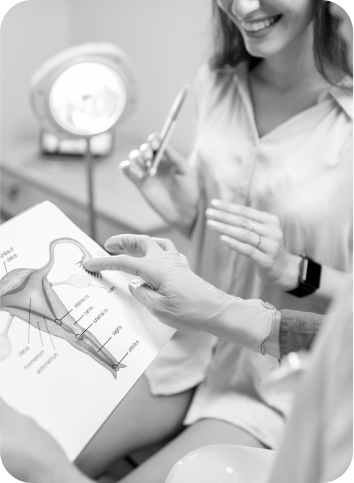

Curettage of the uterine cavity is a gynecological procedure in which the doctor removes tissue from the inner surface of the uterus using an instrument called a curette.
This procedure is performed for a variety of reasons, including the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of gynecological problems.
It is the removal or evacuation of a cyst formed from the so-called Bartholin’s glands located on external genitalia
at the entrance to the vagina with a scalpel. After elimination of bleeding
the wound is sutured with an absorbable suture.


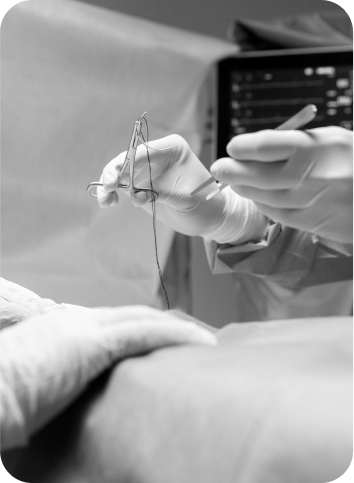
Excision from vulva is a surgical procedure that is performed
to remove unwanted lesions, cysts, tumors or other problems from the vulvar area in women. This procedure is often performed for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons,
if adverse changes or symptoms are detected.
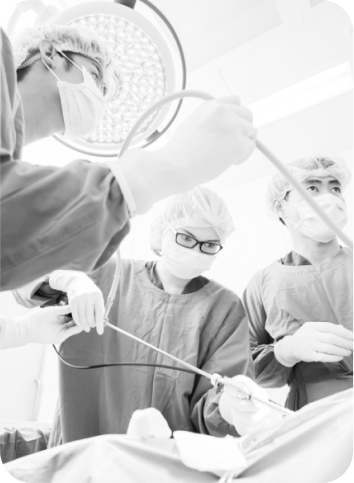
It is a modern endoscopic surgical technique in which
an optical system with a camera and cold light is introduced into the uterine cavity under short intravenous anesthesia. Using advanced coagulation tools, larger formations such as polyps, knots or septa in the uterine cavity are removed. The great advantage of this operation is its gentleness, which allows us to preserve the uterus.



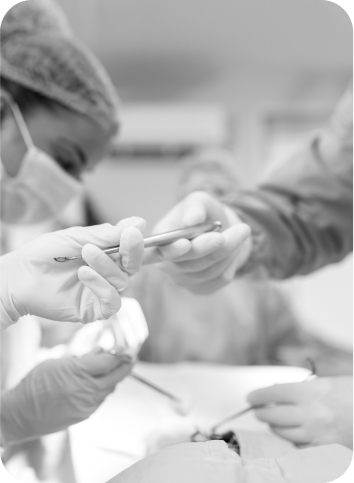
It is a surgical correction of anomalies in various shapes and sizes of the labia minora and vaginal entrance. Performs
for aesthetic or functional reasons. Edited are
also scars after childbirth or birth injuries. Operation
is mainly performed under short intravenous anesthesia. Inquire about the current reimbursement by the insurance company for this procedure.
These are endoscopic operations that are performed under general anesthesia. Individual optical and surgical instruments are introduced into the abdominal cavity through 0.5 to 1 cm punctures. Laparoscopy is used diagnostically in cases of
persistent lower abdominal pain, endometriosis, examinations before the IVF program (artificial insemination), adhesions, etc.
As a surgical and medical procedure, it is used in the removal of ovarian cysts, endometriotic deposits, and myomatous nodes. Laparoscopy is a possible surgical option even when removal of the uterus is indicated.



This is the application of a special tape that will change the topographic conditions of the urethra to its original position,
ensuring the retention of urine postoperatively. The vaginal incision is sutured with absorbable material. There is no need to remove the stitches.
It is plastic surgery of the external genitalia and vagina with a scalpel. The skin and mucous membranes are sutured with absorbable material. The operation is performed in order to reconstruct the anatomical proportions of the pelvic floor. It is a health related procedure.



It is a specialized urogynecological procedure in which implants (mesh) are inserted into the structures of the pelvic floor, which are then fixated with cell growth. This creates a permanent reconstruction of the structures of the pelvic floor (the most modern solution for vaginal plastic surgery).

SOFYC Clinic s.r.o. | Bardejovská 24 | 080 06 Prešov